
Polaris atmospheric network: in May 2018, the Ministry of Ecology and Environment issued the "iron and steel enterprises ultra-low emission transformation work program (draft for comment)", proposed steel sintering (pellet) flue gas particulate matter, sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxide emission concentrations are not higher than 10, 35, 50mg/m3. September 2018, Hebei Province, the iron and steel industry air pollutants ultra-low emission standards officially released to the public. The standard was significantly tightened a few days ago, and local standards in other provinces and cities are in the pipeline, and the transformation deadline is approaching step by step. The second session of the 13th National People's Congress opened at 9 a.m. on March 5 in the Great Hall of the People, on environmental protection Premier Li Keqiang said this: strengthen pollution prevention and ecological construction, and vigorously promote green development. Grow the green environmental protection industry. Accelerate the thermal power, steel industry ultra-low emission transformation, the implementation of heavy pollution industry to meet the standard emission transformation.
The steel industry also needs to accelerate the pace and quickly achieve ultra-low emissions! At present, most existing steel enterprises need to install additional sinter flue gas denitrification systems. Under the current situation and conditions, sintering additional flue gas denitrification system should be combined with the specific project situation, and the process technology route should be selected carefully and reasonably. Due to the instability of sintering process and raw material composition and ratio, it leads to large flow of flue gas, large changes in sulfur dioxide concentration, complex flue gas composition, low flue gas temperature and large range of changes. SCR (Selective Catalytic Reduction) is the most widely used and most mature technology. It has no by-products and does not form secondary pollution.
The current mainstream steel sintering SCR denitrification process is as follows.
1) Pelletizing, sintering → main extractor fan → (head electric dust collector) → GGH → medium and high temperature
system → GGH → desulfurization system → dust removal system → induced draft fan → stack
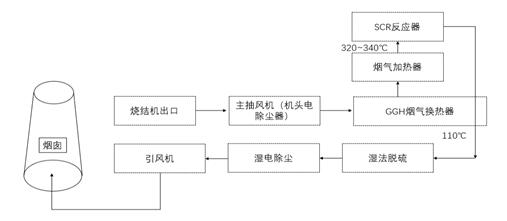
Features.
Use the high flue gas temperature coming out of the electric dedusting at the head to reduce the heating up operation cost. The heat exchanger is used to raise the temperature to 320-340℃ for medium and high temperature denitrification, and the flue gas after denitrification is cooled down by heat exchange technology for wet flue gas desulfurization and dust removal. This program has a large one-time investment, but due to its mature individual process and obvious desulfurization and denitrification efficiency.
In the SCR denitrification system, the flue gas contains 80-200mg/Nm3 of dust, with more than 10% of alkaline earth metal elements, and the operation process will accelerate catalyst deactivation and deterioration. Due to the special nature of the process, the SCR system is arranged after the electrostatic precipitator and before the desulfurization unit, a large amount of sticky dust plus a small portion of hydrogen sulfate ammonia generation block the lower heat exchanger or catalyst layer, and the pressure differential rises suddenly, which seriously affects the long and stable operation of the overall system.
2) Pelletizing and sintering → main extract fan → (head electrostatic precipitator) → desulfurization system → dust removal system → GGH → medium and low temperature SCR denitration system → GGH → denitration induced draft fan → stack
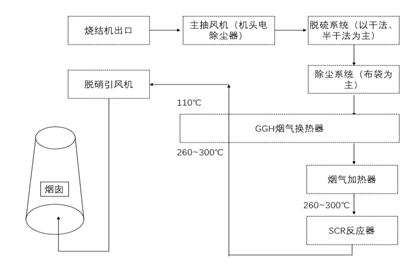
Features.
The SCR system is arranged after the dust and desulfurization unit, and the sintered flue gas enters the desulfurization and dust removal unit first after electrostatic dedusting, and then enters the SCR system. In the SCR system, the flue gas temperature is raised to about 260-300℃ through the heating device into the SCR reactor catalyst layer for denitrification, and the flue gas coming out is cooled down by heat exchange with the low temperature flue gas in the SCR inlet flue and discharged through the stack. At this point, the flue gas is low in sulfur and dust, and the toxic effect on the catalyst is greatly reduced. At present, 70% of the market adopts denitrification process after desulfurization. However, the catalytic activity of catalysts in low and medium temperatures is much higher, and conventional vanadium and titanium catalysts are not effective in low temperature activity. In addition, when the flue gas is below 300℃, ammonia sulfate will dew up and block the catalyst micropores or form a pile of adhesion and blockage, so it needs to be warmed up periodically to pyrolyze ammonia sulfate and activate the catalyst, which will greatly increase the operation and maintenance cost.
Anhui Yuanchen Technology has been committed to air pollution control, taking the lead in developing low temperature denitrification catalyst, which was successfully applied in Beijing Yanqing heating in 2015. After that, it was applied in Fengfeng Hexin mine, Hebei Longfeng Mountain 1#, 2# sintering, Hebei Jingye Steel, Xiwang Metal, Wu'an Yuhua Steel, Anfeng Steel, Jiangsu Danyang, Tangshan Tianzhu Steel, Shanxi Hongda, Shanxi Zhongsheng and other projects to promote the development process of denitrification in the steel industry, to win the battle of blue sky, continue to make efforts and escort.