
On September 22, 2020, President Xi Jinping delivered a speech at the 75th General Debate of the United Nations General Assembly, pledging that "China will increase its autonomous national contribution, adopt stronger policies and measures, and strive to peak CO2 emissions by 2030 and achieve carbon neutrality by 2060." On October 29, the Fifth Plenary Session of the 19th CPC Central Committee adopted the "Proposal of the CPC Central Committee on Formulating the 14th Five-Year Plan for National Economic and Social Development and the 2035 Vision". Since the Paris Agreement established the long-term goal of "keeping the global average temperature rise within 2°C (compared to pre-industrial levels) during this century, and striving to keep the temperature rise within 1.5°C," the academic community has conducted in-depth discussions and studies.
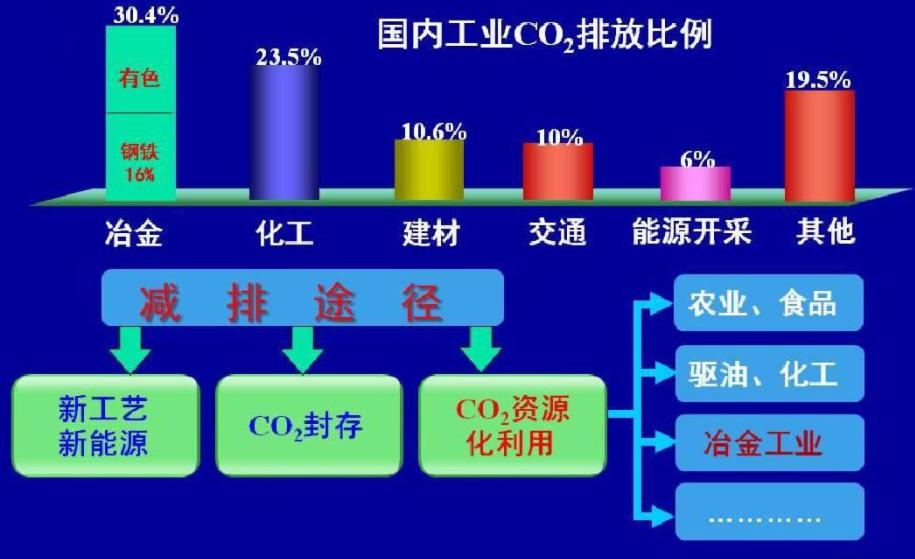
The rapid increase of carbon dioxide concentration caused by the burning of fossil fuels directly contributes to global warming, which is the biggest problem of global temperature rise control and poses a great threat to human production and life. Therefore, how to reduce the concentration of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere has become a common concern in the world. At present, there are three main options to reduce the concentration of CO2 in the atmosphere: (1) reducing CO2 emissions to solve the problem at the source; (2) capturing CO2 in the atmosphere and then storing it using methods such as deep burial; (3) using CO2 as a raw material to produce high value-added related derivative products. Despite being an industrial waste gas, CO2 can also be a substantial, cheap, non-toxic and renewable carbon resource. The reuse of carbon dioxide as a raw material has important research value and significance both in terms of energy use and environmental protection.
There are several methods to recycle carbon dioxide.
(1) Photocatalytic reduction: The photocatalytic reduction of CO2 has been of great interest to researchers in recent decades, and its core concept is to use sunlight and simulate the entire natural environment in a light-closed cycle. This approach is considered advanced because it is a reaction that takes place under relatively mild conditions, i.e., at room temperature and atmospheric pressure, and without additional energy input.
(2) Electrocatalysis: Electrochemical reduction of CO2 (CO2-RR) is an innovative technology that allows the conversion of CO2 into value-added chemical products under mild conditions by directly using electrical energy in order to create a potential difference between two electrodes.
(3) Solar thermochemical conversion: Solar energy is a renewable source of energy because no additional energy is required and there are no negative effects, thus the use of direct solar irradiation to convert CO2 is probably the most efficient method. Direct solar energy conversion can be divided into two types: thermal conversion - sunlight is absorbed and converted into heat energy and then extracted; quantum conversion - can be directly acquired by photon absorbers (e.g., semiconductors or organic compounds) and then converted to output, i.e., photocatalysis as described above. .
(4) Biochemical conversion: The biochemical conversion of CO2 is essentially the production of biofuels through "natural" photosynthesis, which is very attractive for the production of chemicals or fuels because it can occur entirely in its natural state. Microalgae solutions, for example, not only have no additional land use requirements, but also improve air quality, require very little water and, most importantly, are less expensive to produce than petroleum-based fuels, making them quite competitive.
(5) Thermocatalysis: Hydrogen has high energy and can be used as a reactant for CO2 conversion. With the development of renewable energy sources (wind, solar, etc.), the source of hydrogen has been solved by electrolysis of water through surplus electricity. Therefore, carbon dioxide hydrogenation is of great interest because it can be converted on a large scale to produce value-added hydrocarbons. In addition, various hydrocarbons can be produced indirectly through the conversion of CO2 hydrogenation into both methanol and MTH.

Anhui Yuanchen Environmental Technology Co., Ltd (hereinafter referred to as "Yuanchen Technology") is a high-tech enterprise integrating R&D, production and sales of dust removal bags and denitrification catalysts. Over the past sixteen years, Yuanchen Technology has been focusing on the environmental protection field, and now has 4 international PCT, 33 authorized invention patents and 77 invention patents in process, among which many products such as "dust removal and denitrification integrated technology products" have been awarded the Scientific Progress Award of Anhui Province. Our dust removal bags (mainly PPS, PTFE, P84 and composite series filter needle felt) and SCR denitrification catalysts have been widely used in cement, steel, glass kilns, waste incineration power generation, biomass power generation, non-ferrous metal smelting and other industries. In the future, Yuanchen Technology will be guided by "becoming the guardian of global ecological environment", always rooted in environmental protection, and insist on the great cause of guarding the blue sky and white clouds. Leveraging on the national ecological civilization construction pattern, we will continue to deepen technology, optimize management, strengthen brand, refine industry and solidify advantages, and create synergistic value for industry through comprehensive and integrated governance and services.